Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) is a crucial concept that involves strategies and actions to reduce the risks and impacts of disasters on communities. With increasing natural hazards and climate-related disasters, DRR has become a global priority.
In this article, we’ll dive into the key concepts of DRR, its frameworks, challenges, and the role of communities in building resilience.
Introduction
Disasters, whether natural or human-made, have long-lasting consequences. They disrupt lives, destroy infrastructure, and have economic impacts that can take years to recover from.
Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) is the proactive approach to minimizing these impacts and protecting vulnerable populations.
By understanding and mitigating risks, communities can better prepare for, respond to, and recover from disasters.
Definitions And Related Concepts
What Is Disaster Risk Reduction?
Disaster Risk Reduction refers to the systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and reducing risks associated with disasters.
It includes prevention, mitigation, and preparedness efforts that seek to decrease the negative consequences of disasters on people, property, and livelihoods.
Core Concepts In DRR
- Resilience: Resilience refers to the capacity of a system, community, or society to adapt to and recover from disasters.
Building resilience involves reducing vulnerabilities and ensuring that communities can withstand future risks. - Vulnerability: Vulnerability describes the factors that make people or systems more susceptible to harm during a disaster.
These factors can include geographic location, economic status, or lack of preparedness. - Risk Reduction and Mitigation: These strategies aim to lessen the negative effects of disasters. Risk reduction involves identifying and reducing exposure to hazards, while mitigation involves measures like infrastructure upgrades to minimize the damage caused by disasters.
- Climate Change Adaptation: This is the process of making adjustments in systems, practices, and policies to cope with the changing climate.
DRR and climate change adaptation are interconnected, as both seek to reduce risks and enhance resilience.
Understanding Disaster Risk
Components Of Risk
Disaster risk is composed of three primary elements: hazard, vulnerability, and exposure.
| Concept | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Hazard | A natural or human-induced event that has the potential to cause harm. | Earthquakes, floods, wildfires, industrial accidents, chemical spills. |
| Vulnerability | The degree of susceptibility of people, systems, or assets to the harmful effects of a hazard. Influenced by factors like socioeconomic status, health, and location. | Poor communities, elderly populations, areas with poor infrastructure, or those lacking resources. |
| Exposure | The presence of people, infrastructure, and assets in areas that are at risk from hazards. | Cities located in floodplains, coastal areas prone to hurricanes, or areas near industrial facilities. |
Risk Assessment
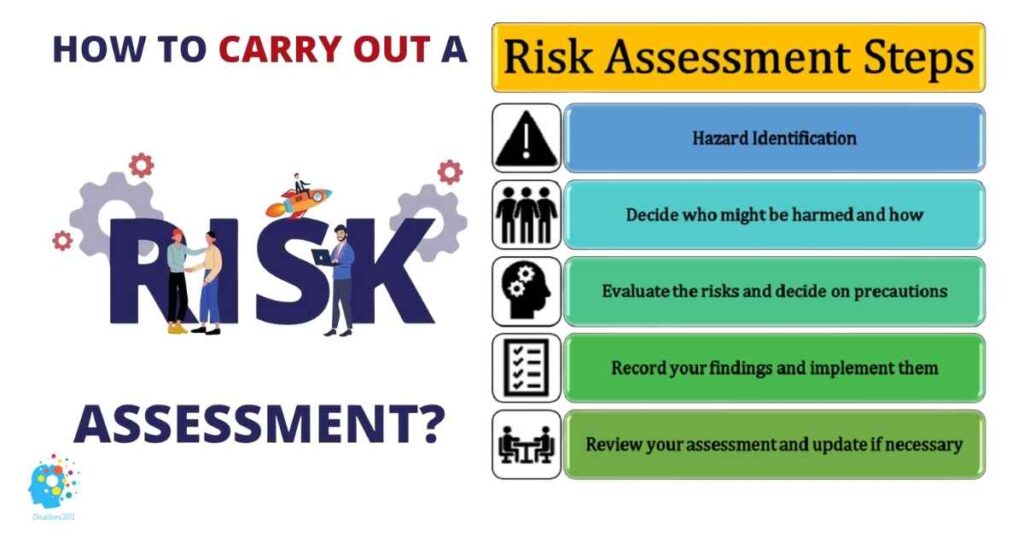
Risk assessment tools are used to identify potential hazards, evaluate the vulnerability of systems, and understand the exposure of people and assets to those hazards.
Effective risk assessments provide a foundation for risk reduction strategies and preparedness planning.
Risk Drivers
- Climate Change: Changing climate patterns, such as increased frequency of storms and floods, are major drivers of disaster risk.
- Poor Urban Planning: Inadequate infrastructure and overcrowded cities can amplify the impacts of disasters.
- Human Behavior: Human activities, such as deforestation, contribute to increased disaster risks.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty and inequality often make communities more vulnerable to disasters, as they lack resources to prepare or recover.
Types Of Risks
- Deterministic Risk: Risks that are predictable based on known factors, such as the impact of an earthquake in a seismically active area.
- Probabilistic Risk: Risks that are assessed using statistical methods, providing a likelihood of occurrence over time.
- Intensive and Extensive Risks: Intensive risks involve high-impact, low-frequency events (e.g., major earthquakes), while extensive risks refer to smaller, more frequent disasters (e.g., floods, storms).
Frameworks And Goals For DRR
Sendai Framework For Disaster Risk Reduction

The Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction provides a comprehensive approach to reducing disaster risk.
Adopted by the UN in 2015, it sets out clear priorities for action and targets for reducing disaster risks by 2030. Its key principles include:
- Understanding disaster risk.
- Strengthening disaster risk governance.
- Investing in risk reduction for resilience.
- Enhancing disaster preparedness.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)

The SDGs and DRR are closely linked. DRR is crucial for achieving Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Goal 13: Climate Action, as both focus on building resilient infrastructure and reducing disaster impacts.
Community Based Disaster Risk Reduction
Community Based Disaster Risk Reduction (CBDRR) is an approach that empowers local communities to take an active role in managing and reducing the risks associated with natural and human-made disasters.
It involves the participation of community members in identifying hazards, assessing vulnerabilities, and developing strategies to mitigate risks. By focusing on local knowledge, resources, and capacities, CBDRR aims to build resilience at the grassroots level, ensuring that disaster risk reduction efforts are tailored to the specific needs and context of the community.
This approach emphasizes collaboration between communities, governments, and humanitarian organizations to enhance preparedness, response, and recovery.
Community Engagement And Participation

Incorporating community-based approaches in DRR ensures that local needs and capacities are considered.
Empowering vulnerable groups, such as children and women, to participate in DRR initiatives builds local resilience and enhances preparedness.
Governance And Leadership

Effective governance and leadership are essential for coordinating DRR efforts.
Governments, local authorities, and stakeholders must collaborate to create and implement policies that reduce risks and promote resilience.
Gender Considerations

Gender-specific vulnerabilities should be addressed in DRR strategies.
Women, for instance, often face disproportionate risks due to social and economic factors, making it crucial to incorporate gender-sensitive approaches in disaster risk management.
Economic Considerations
Economic Costs Of Disasters
The economic impact of disasters is rising, with climate related events causing significant damage to infrastructure and livelihoods.
Inaction in DRR can result in higher recovery costs and greater losses.
Financing DRR
Innovative funding mechanisms are required to support DRR efforts, including risk disclosure initiatives and increased investments in risk-reducing infrastructure.
Effective Strategies For DRR

Priorities For Action (Sendai Framework)
The Sendai Framework’s priorities for action guide global efforts in DRR:
- Understanding disaster risk.
- Strengthening governance for resilience.
- Investing in disaster risk reduction.
- Enhancing disaster preparedness.
Risk Reduction Approaches
- Prevention: The goal of prevention is to avoid disasters whenever possible. This includes regulating land use and building codes.
- Mitigation: involves taking steps to reduce the impact of disasters, such as flood control infrastructure and building earthquake-resistant structures.
- Transfer: Transferring risks through tools like insurance can help communities and businesses manage the financial impact of disasters.
- Preparedness: Effective preparedness involves developing response plans, conducting drills, and ensuring that communities are ready to act when a disaster strikes.
Tools And Resources For DRR
Several resources and tools are available for DRR, including hazard and vulnerability assessments, capacity building initiatives and guidelines from organizations like the UNDRR.
Examples And Case Studies
Successful DRR Initiatives
- Bangladesh’s National Plan for Disaster Management: Bangladesh has implemented an integrated approach to disaster risk management, significantly reducing vulnerability and enhancing resilience.
- The European Union’s Civil Protection Mechanism: This mechanism provides a collaborative approach to disaster preparedness and response across EU member states.
Lessons Learned
Effective DRR requires a mix of strong governance, community involvement, and continuous monitoring.
Key lessons include the importance of local knowledge and the need for inclusive approaches.
DRR And Climate Change Adaptation
Project Planning
Integrating DRR into development projects ensures that climate change and disaster risks are considered early in the planning process.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessments must differentiate between hazard, vulnerability, and capacity assessments to create a clear understanding of disaster risks.
Monitoring And Evaluation

Global Targets And Indicators
The Sendai Framework includes seven global targets for reducing disaster risk.
Monitoring progress against these targets helps track improvements in resilience.
Monitoring Tools
Tools like the Sendai Framework Monitor help track the implementation of DRR strategies and measure global progress.
DRR Capacities In Different Contexts
Comparing Capacities
There are disparities in DRR capacities between richer and poorer countries.
Wealthier nations typically have better resources, infrastructure, and governance systems in place to reduce risks, while poorer countries often face significant challenges in building resilience.
Conclusion
Disaster Risk Reduction is an essential framework for reducing disaster risks and minimizing their impacts.
By focusing on understanding risks, strengthening governance, and investing in resilience, communities can better prepare for future disasters.
Global initiatives like the Sendai Framework and SDGs play a pivotal role in driving DRR efforts.
It’s time to prioritize DRR. Governments, organizations, and individuals must collaborate to invest in DRR strategies that not only save lives but also promote sustainable development for future generations.
References
- UNISDR – Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction
- UNDRR – Disaster Risk Reduction Knowledge Centre
- World Bank – Disaster Risk Management (DRM)
- IFRC – Disaster Risk Reduction
- UNDP – Disaster Risk Reduction and Resilience
- The International Disaster Emergency Service (IDES) – DRR Tools
- Center for Disaster Philanthropy (CDP)
- The Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) – 2005-2015
- WHO – Health Emergency and Disaster Risk Management
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Are the 4 types Of Disaster Risk Reduction?
Prevention, Mitigation, Preparedness, and Transfer.
What Are The Key Components Of Risk Reduction?
Risk identification, vulnerability assessment, risk mitigation, and preparedness.
How Is Disaster Risk Management Different From Disaster Risk Reduction?
Disaster risk management focuses on managing risks during and after a disaster, while DRR focuses on reducing risks before they occur.
What Are The 4 Ts Of Risk Mitigation?
Transfer, Treat, Tolerate, Terminate.
What Are Examples Of DRR In Practice?
Building flood barriers, developing early warning systems, and implementing zoning laws.
What Is Difference Between Disaster Management And Disaster Risk Management?
Disaster Management focuses on responding to and managing the aftermath of a disaster. It includes emergency response, recovery, and rehabilitation efforts.
Disaster Risk Management involves proactive measures to reduce the likelihood and impact of disasters, including risk assessment, mitigation, and preparedness planning.
What Is Disaster Risk Reduction?
Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR): Refers to the strategies and actions taken to minimize the impact of natural and human-made disasters.
It includes measures like risk assessment, preparedness, and mitigation to prevent disasters or reduce their severity.
What Is Difference Between Disaster Risk Reduction and Disaster Management?
Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) focuses on preventing or reducing the risk of disasters before they occur. It emphasizes risk reduction, preparedness, and resilience building.
Disaster Management involves responding to and recovering from disasters after they happen, addressing immediate impacts and long-term recovery.
What Is Importance Of Disaster Risk Reduction To Humanity?
Disaster Risk Reduction is crucial for saving lives, reducing economic losses, and building resilient communities.
It helps prevent or minimize the impact of disasters, ensuring that societies are better prepared for future events.
What Is Significance Of Disaster Reduction?
Disaster reduction is significant because it reduces vulnerability, enhances community resilience, and prevents loss of life, property, and livelihoods during disasters.
It also promotes sustainable development by mitigating risks in vulnerable areas.
What Is Your Responsibility As A Citizen In Disaster Risk Reduction?
As a citizen, your responsibilities include staying informed about disaster risks, following safety guidelines, preparing an emergency plan, and participating in community preparedness initiatives.
You can also raise awareness and support local resilience building efforts.
What Does The 2014 IPCC Fifth Assessment Report say About Climate Change Adaptation And Disaster Risk Reduction?
The 2014 IPCC Fifth Assessment Report highlights that climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction are interconnected.
It stresses the need to integrate both approaches to reduce vulnerability to climate impacts and strengthen resilience to disasters.
What Is The Importance of Disaster Risk Reduction And Management Awareness?
Awareness of disaster risk reduction and management is essential for ensuring communities are prepared, resilient, and able to respond effectively to disasters.
It helps reduce the impact of disasters and improves recovery efforts by fostering better planning and resource allocation.
What Is The Relationship Between Disaster Risk Assessment and Disaster Risk Reduction?
Disaster risk assessment identifies the potential hazards, vulnerabilities, and exposures in a community.
This information forms the foundation for disaster risk reduction strategies, enabling informed decision-making to minimize or eliminate risks.
Why Do We Need To Study Disaster Risk Reduction And Management?
Studying DRR and management is essential to understand how to prevent, prepare for, and respond to disasters.
It equips individuals and communities with the knowledge and tools to reduce risks, mitigate impacts, and improve resilience to disaster.
What Is Role of the Government in Disaster Risk Reduction?
The government plays a critical role in disaster risk reduction by creating and enforcing policies, providing funding for preparedness and mitigation efforts, coordinating response activities, and ensuring that communities are equipped with the resources and knowledge to reduce risks effectively

